摘要:在本节中,你将学习如何使用 Python 的 try...except 语句来优雅地处理异常。
在 Python 中,主要有两种错误:语法错误和异常。
Python中的语法错误
当你编写了无效的 Python 代码时,将会出现语法错误。例如:
current = 1
if current < 10
current += 1如果你尝试运行这段代码,将会出现以下错误:
File "d:/python/try-except.py", line 2
if current < 10
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax在这个例子中,由于 if 语句后面缺少冒号(:),Python 解释器检测到了该错误。
Python 解释器会显示发生错误的文件名和行号,以便你进行修正。
Python代码中的异常
即使你的代码语法有效,在执行过程中也可能导致错误。
在 Python 中,执行期间发生的错误称为异常。异常的成因主要来自代码执行的环境。例如:
读取一个不存在的文件。
连接一个离线的远程服务器。
用户输入错误。
当发生异常时,程序不会自动处理它。这会导致出现错误消息。
例如,以下程序用于计算销售增长率:
# get input net sales
print('Enter the net sales for')
previous = float(input('- Prior period:'))
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
# calculate the change in percentage
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
# show the result
if change > 0:
result = f'Sales increase {abs(change)}%'
else:
result = f'Sales decrease {abs(change)}%'
print(result)其工作原理:
首先,提示用户输入两个数字:上一期和当期的净销售额。
然后,计算销售增长率(百分比)并显示结果。
当你运行该程序并输120'作为当期净销售额时,Python 解释器将输出以下内容:
Enter the net sales for
- Prior period:100
- Current period:120'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:/python/try-except.py", line 5, in <module>
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
ValueError: could not convert string to float: "120'"Python 解释器显示了一个包含异常详细信息的回溯信息:
导致异常的源代码文件路径(
d:/python/try-except.py)。导致异常的确切代码行(第 5 行)。
导致异常的语句
current = float(input('- Current period:'))。异常类型
ValueError。错误消息
ValueError: could not convert string to float: "120'"(无法将字符串120'转换为浮点数)。
由于 float() 无法将字符串 120' 转换为数字,因此 Python 解释器抛出了 ValueError 异常。
在 Python 中,异常具有不同的类型,例如 TypeErrorNameError 等。
try...except语句处理异常
为了让程序更加健壮,你需要在异常发生时对其进行处理。换句话说,你需要捕获异常并通知用户,以便他们能够修复它。
一个好的处理方法是不要显示 Python 解释器返回的内容。相反,你应该用一个更用户友好的消息来替换那个错误消息。
为此,你可以使用 Python 的 try...except 语句:
try:
# code that may cause error
except:
# handle errorstry...except 语句的工作原理如下:
try子句中的语句首先执行。如果没有发生异常,则跳过
except子句try语句的执行完成。如果
try子句中的任何语句发生异常,则跳过该子句的其余部分,并执行except子句。
以下流程图说明了 try...except 语句:
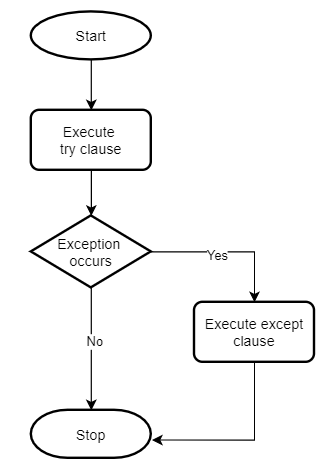
因此,要使用 try...except 语句处理异常,你可以将可能引发异常的代码放在 try 子句中,而将处理异常的代码放在 except 子句中。
以下是如何重写程序并使用 try...except 语句来处理异常的方法:
try:
# get input net sales
print('Enter the net sales for')
previous = float(input('- Prior period:'))
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
# calculate the change in percentage
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
# show the result
if change > 0:
result = f'Sales increase {abs(change)}%'
else:
result = f'Sales decrease {abs(change)}%'
print(result)
except:
print('Error! Please enter a number for net sales.')如果你再次运行该程序,并输入一个非数字形式的净销售额(值),程序将输出你在 except 块中指定的提示信息;
Enter the net sales for
- Prior period:100
- Current period:120'
Error! Please enter a number for net sales.捕获特定类型的异常
当你将上一期的净销售额输入为零时,你会收到以下信息:
Enter the net sales for
- Prior period:0
- Current period:100
Error! Please enter a number for net sales.在这种情况下,上一期和当期的净销售额都是数字,但程序仍然输出了一条错误信息。这表明一定发生了另一个异常。
try...except 语句允许你处理特定的异常。要捕获选定的异常,你可以在 except 关键字后指定异常的类型:
try:
# code that may cause an exception
except ValueError as error:
# code to handle the exception例如:
try:
# get input net sales
print('Enter the net sales for')
previous = float(input('- Prior period:'))
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
# calculate the change in percentage
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
# show the result
if change > 0:
result = f'Sales increase {abs(change)}%'
else:
result = f'Sales decrease {abs(change)}%'
print(result)
except ValueError:
print('Error! Please enter a number for net sales.')当你运行程序并为净销售额输入一个字符串时,你会得到同样的错误信息。
然而,如果你为上一期的净销售额输入零:
Enter the net sales for
- Prior period:0
- Current period:100……你会得到以下错误信息:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:/python/try-except.py", line 9, in <module>
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero这次你遇到了 ZeroDivisionError(零除错误)异常。这个除零异常是由以下语句引起的:
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous原因是 previous为零。
处理多种异常
try...except 结构允许你通过指定多个 except 子句来处理多种异常:
try:
# code that may cause an exception
except Exception1 as e1:
# handle exception
except Exception2 as e2:
# handle exception
except Exception3 as e3:
# handle exception 这使你能够针对每种异常类型做出不同的响应。
如果你希望对某些类型的异常做出相同的响应,可以将它们归为一个 except 子句中:
try:
# code that may cause an exception
except (Exception1, Exception2):
# handle exception以下示例展示了如何使用 try...except 来处理 ValueError 和 ZeroDivisionError 异常:
try:
# get input net sales
print('Enter the net sales for')
previous = float(input('- Prior period:'))
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
# calculate the change in percentage
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
# show the result
if change > 0:
result = f'Sales increase {abs(change)}%'
else:
result = f'Sales decrease {abs(change)}%'
print(result)
except ValueError:
print('Error! Please enter a number for net sales.')
except ZeroDivisionError:
print('Error! The prior net sales cannot be zero.')当为上一期的净销售额输入零时:
Enter the net sales for
- Prior period:0
- Current period:120……你会得到以下错误:
Error! The prior net sales cannot be zero.通过在异常处理列表的末尾放except Exception来捕获其他一般性错误,是一种良好的做法;
try:
# get input net sales
print('Enter the net sales for')
previous = float(input('- Prior period:'))
current = float(input('- Current period:'))
# calculate the change in percentage
change = (current - previous) * 100 / previous
# show the result
if change > 0:
result = f'Sales increase {abs(change)}%'
else:
result = f'Sales decrease {abs(change)}%'
print(result)
except ValueError:
print('Error! Please enter a number for net sales.')
except ZeroDivisionError:
print('Error! The prior net sales cannot be zero.')
except Exception as error:
print(error)总结
使用 Python 的
try...except语句优雅地处理异常。在
except块中尽可能使用特定的异常类型。使用
except Exception语句来捕获其他异常。
